
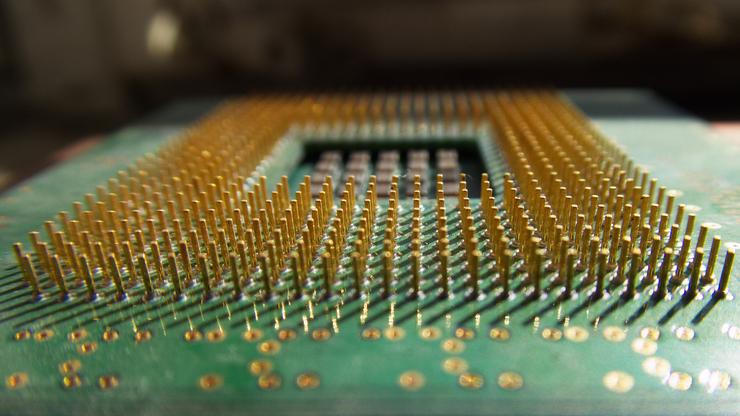
The 6502 is the famous processor found at the core of such influential. 1 day ago &0183 &32 The minuscule fluctuations of seemingly empty space can be controlled just enough to make the building blocks of a new type of computer. But some physicists and engineers think we might be bumping up against some fundamental physical limits when it comes to transistor size. to make a complete, working transistor-scale replica of the classic MOS 6502. These will use transistors measuring a mere 32 nanometers in width. Intel and other microprocessor manufacturers are already working on the next generation of chips. By the 2010s, Intel produced microprocessors with transistors measuring only 45 nanometers wide. They put the mask over the silicone and then apply. They start with a silicon wafer, and then they build masks which are plates with very very small holes cut in it with a laser. But that raises an interesting question: How small can transistors - and by extension, CPUs - get? In 1947, a single transistor measured a little over one-hundredth of a meter high. Its not really several small electronics jammed into one space all the transistors are built together in one unified process. These days, the number of transistors doubles every 24 months. But it hasn't kept up with the pace Moore observed. In quantities of thousands, millions, and even billions, transistors are interconnected and embedded into tiny chips to create computer memories, microprocessors, and other complex ICs. Since Moore's observation, the shrinking trend has continued. In 1965, Intel co-founder Gordon Moore predicted that the number of transistors that could fit on a computer chip would grow exponentially and they did, doubling about every two years. In small, discrete quantities, transistors can be used to create simple electronic switches, digital logic, and signal amplifying circuits. Without transistors, we would still be using vacuum tubes and mechanical switches to make calculations. It's because of these small transistors that we have electronic devices like personal computers, smartphones and mp3 players. The transistor only allows the source current to flow through it to the drain if there is current across the gate. To perform calculations in binary, they use what’s called a transistor. They only understand two states: on and off.

Like clockwork, engineers were finding ways to reduce the size of transistors. Modern microprocessors typically include on-chip cache memories. Starting Small Computers operate in binary. It makes calculations and processes data.īy the 1960s, computer scientist (and Intel co-founder) Gordon Moore made an interesting observation: He noticed that every 12 months, engineers were able to double the number of transistors on a square-inch piece of silicon. If you compare a computer to a human being, the microprocessor would be the brain. In turn, the integrated circuit paved the way for the development of the microprocessor.

In 1958, engineers attached two transistors to a silicon crystal and created the world's first integrated circuit.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
